Heat Staking Machine
Heat Staking is a pulsed heat process to join two or more parts, of which one is at least made out of plastic. The process is to deform the plastic material using heat and force at a set process time. The bond is made by partially de-forming the plastic part in order to fix the other. Heat Staking equipment makes it easy to bond metal to plastic and is commonly used in high volume/low cost applications like automotive, IT and consumer appliances.
Process Explained
De-forming the plastic is achieved by heating it to a temperature above the glass transition temperature via the use of super-heated air or a thermode and then applying pressure in order to create the stake. After the stake has been formed the plastic should be cooled down again below the glass transition temperature. This cooling is done under constant pressure to ensure good fixation of the parts. Cooling can be done with the use of compressed air when using a thermode.
Heat is used to make it easier to create the stake. Heat control is critical, especially for glass filled plastics which often have a process window smaller than 10 degrees Celsius. When temperatures are too high the glass fibers come out of the plastic leading to a rough surface and sticking to the thermode. If the temperature is too low the plastic will crack due to cold deformation.
Benefits
- Similar and dissimilar materials may be joined: metal to metal, plastic to plastic, metal to plastic
- Accurate control operating within a small process window
- Local heating resulting in no damage to surrounding materials
- Processing of glass-filled materials
- No mechanical vibration
- Many heat stake shapes possible through custom designed tools
Applications
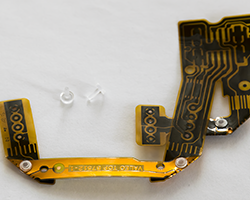
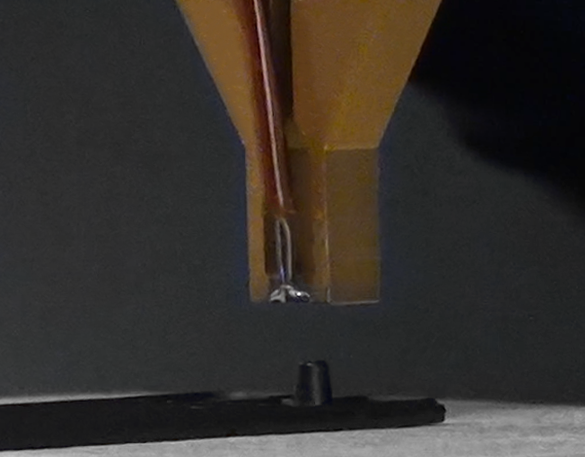
Leading Manufacturer of Heat Staking Equipment
C-Tech is a leading manufacturer of heat staking equipment, designed to deliver precision and efficiency in your production processes. Our advanced heat staking machines ensure consistent and reliable results when joining thermoplastics with other materials, making them ideal for industries requiring high-quality assemblies. Engineered with state-of-the-art technology, C-Tech’s heat staking equipment offers unparalleled performance, flexibility, and durability to meet diverse manufacturing needs. Choose C-Tech for innovative heat staking machines that optimize your workflow and deliver superior results every time.
Contact Us Today!
Ready to elevate your heat staking process? Contact C-Tech today to learn more about our industry-leading equipment and find the perfect machine for your needs!
